
Publications

Impact of Intrapericardial Fluid on Lesion Size During Epicardial Radiofrequency Ablation: A Computational Study
Background and aims: Epicardial RFA is often required when ventricular tachyarrhythmias originate from epicardial or subepicardial substrates that cannot be effectively ablated endocardially. Our objective was to evaluate the impact of intrapericardial fluid accumulation on the lesion size in the myocardium and the extent of thermal damage to adjacent structures, particularly the lung...

Thermal side effects during pulsed field ablation: An analysis using computer modeling
Aims:
Pulsed field ablation (PFA) is described as non-thermal, but data from oncology and cardiology show thermal effects occur. The specific waveform parameters influencing thermal energy development during PFA are unclear. The aim of this study is to numerically evaluate the thermal effects of PFA on myocardial and oesophageal tissue at various peak voltage conditions. Methods and results: A ...

Proactive esophageal cooling during radiofrequency cardiac ablation: data update including applications in very high-power short duration ablation
Introduction
Proactive esophageal cooling reduces injury during radiofrequency (RF) ablation of the left atrium (LA) for the treatment of atrial fibrillation (AF). New catheters are capable of higher wattage settings up to 90 W (very high-power short duration, vHPSD) for 4 s. Varying power and duration, however, does not eliminate the risk of thermal injury. Furthermore, alternative energy sou ...
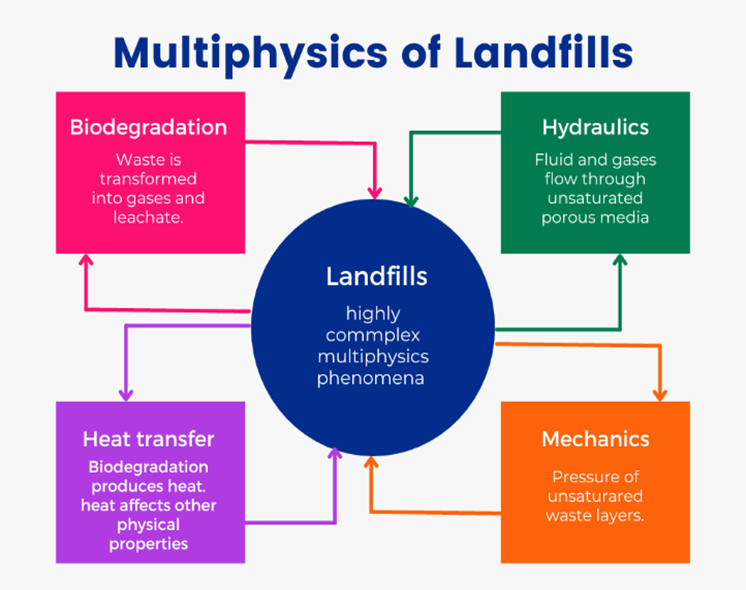
Numerical simulation of waste landfill biodegradation: Fitting experimental data
Landfill remains economically viable for the disposal of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW), however, experiences of failure in several Colombian and global locations, lead to soil, water, and air pollution, harming ecosystems, and biodiversity. Numerical models can help improve the design by considerin...